Since lithium-ion (Lithium-Ion, Li-ion) batteries replaced nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, they have become more and more commonly used in mobile phones, tablet computers, ultra-thin laptops and other portable electronic products. Products require higher and higher battery capacity, but at the same time require smaller and thinner batteries, which makes lithium batteries have a higher capacity density.
Lithium Polymer (LiP) batteries can meet thinner requirements, so their market share continues to increase. In particular, smartphones, tablet computers, and ultra-thin laptops almost all use lithium polymer batteries. However, because lithium-ion batteries can catch fire or even explode under certain abuse conditions, such as overcharge, short circuit and high temperature, they will cause heat and gas to be generated inside the battery, causing the battery to expand, rupture and catch fire. Therefore, lithium The safety of ion batteries has also attracted the attention of manufacturers, end users and management departments.
China and other countries have successively issued their own safety standards for batteries, such as China GBT18287 and GB31241-2014, UL1642 and UL2054 applicable to the United States and North America, EU EN60950 and EN62133, Japan PSE and South Korea KC standards, etc. Standards play a positive role in regulating the market and protecting consumers.
Choose suitable passive protection devices to ensure the safety of lithium batteries
In many cases, battery designers will encounter some problems when choosing passive protection devices, such as whether to use passive protection devices? Which one to use? For lithium batteries, safety standards and performance requirements conflict with each other, and sometimes it is difficult to have the best of both worlds. What should I do?
This article will explain how to choose a suitable passive protection device fuse (Fuse)/Polymeric PosiTIve Thermal Coefficient (PPTC)/MHP-TA (Metal Hybrid PPTC-Thermal AcTIvaTIon Device) to meet safety requirements at the same time. Regulatory standards and host requirements for the charge and discharge performance of lithium batteries, the safety standards in this article take UL2054 as an example.
One-time blown fuse is fragile
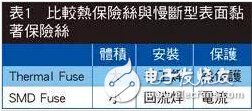
The fuse mentioned here is a one-time blown fuse (fuse), in lithium battery applications usually include thermal fuse (Thermal Fuse) and slow blow type surface mount fuse (SMD Fuse) (Table 1).
The unrecoverable nature of one-time blown fuses makes designers need to be extra cautious when selecting them, so as to avoid damage to the battery due to mistakes during battery assembly, testing and use.
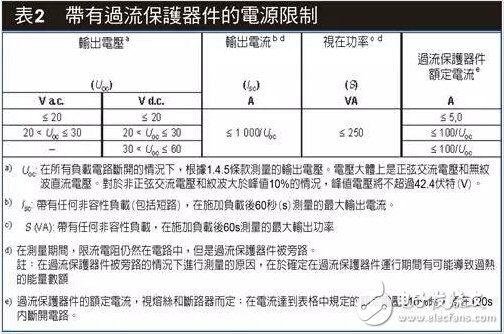
Another main purpose of choosing a slow-blow fuse is the requirement of Limited Power Source (LPS), as shown in Table 2. Generally, a surface-mount type Fuse with a rated current of 5 amperes (A) is selected. Because it can meet the requirements of LPS and battery charging and discharging at the same time, due to the non-recoverability of SMD Fuse, the fusing time of the selected slow-blow type Fuse must be longer than that of the protection IC. The over-current action time is long, so as to ensure that when the protection circuit is working normally, the Fuse will not operate and fuse.
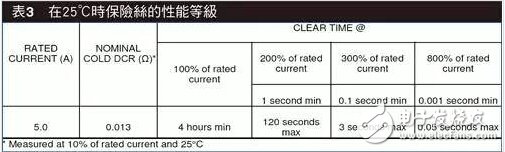
To meet such requirements for protection component suppliers, Fuse must have excellent quality control during the production process to ensure performance consistency. Because LPS limits the maximum specification of Fuse to 5A, it is difficult to meet the high requirements for charging and discharging applications (Table 3).
PPTC performance/safety regulations must be considered comprehensively
PPTC is a positive temperature coefficient thermistor, which is widely used in lithium battery protection circuits. As the capacity of lithium batteries continues to increase, and portable electronic products such as mobile phones continue to increase battery current requirements, the factors that need to be considered when choosing PPTC are also increasing. More and more, on the one hand, it is necessary to meet the product performance requirements, but also to meet the safety requirements of lithium batteries (Figure 1).

Figure 1 There are many factors to consider when choosing a PPTC. To meet the product performance, it must also meet the safety requirements of lithium batteries.
. Assembly method
PPTC is a temperature-sensitive device, so it is necessary to fully consider its assembly method and production process in the battery, such as the setting and effective control of reflow soldering temperature curve, the number of reflow soldering, circuit board dispensing and curing method (UV irradiation or high temperature baking) , Low-temperature injection parameter setting (pressure, temperature and time), and whether there is a manual welding process. PPTC may increase resistance due to pressure and high temperature in these processes, which indirectly affects the holding current and operating characteristics.
Surface mount PPTC is mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB) through reflow soldering. Factors such as pad size, copper foil thickness, trace width, and heating of adjacent components will affect the heat dissipation performance of PPTC, thereby affecting the holding current and operation characteristic.
The strip-shaped PPTC is connected to the lithium battery core electrode and the nickel strip and the PCB board through resistance welding or laser welding. Therefore, the length, width and thickness of the nickel strip will affect the heat dissipation performance, thereby affecting the retention current and operating characteristics of the PPTC (Figure 2).
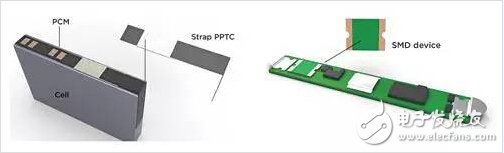
Figure 2 The strip-shaped PPTC is connected to the lithium battery core electrode and the nickel strip is connected to the PCB board
. Safety requirements
When PPTC is used in lithium batteries, LPS has different requirements from Fuse. There are many factors to consider when choosing, especially the high current discharge requirements at high temperature and the overcharge requirements in safety regulations must be met at the same time. Not only the characteristics of PPTC itself must be considered. , It is necessary to carry out an overcharge test with the lithium battery core selected for the specific project. Different manufacturers, different specifications and models of lithium battery cells have different temperature and safety characteristics in the overcharge test. The surface mount PPTC is far away from the battery cell on the circuit board, so it cannot fully sense the temperature change of the battery cell, and it is also affected by the heating of the circuit board wiring and other components. Therefore, in order to meet the safety requirements, choose surface mount When type PPTC, the current specification should be slightly reduced.
For the belt-shaped PPTC, during the battery design and production process, it cannot be subjected to external force and stress on the device; the connection method with the battery cell, the degree of adhesion and the size of the nickel tape will affect whether the battery can pass the safety test (Figure 3) .
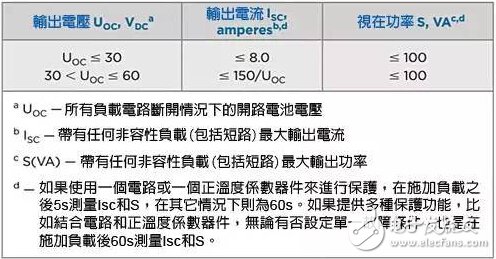
Figure 3 Limitations of power supplies without overcurrent protection devices
MHP-TA has small size / high temperature protection accuracy, suitable for large current needs
MHP-TA is a recoverable temperature protection device with small size and high temperature protection accuracy, so it is suitable for large current needs and is an ideal choice for safety protection of large-capacity lithium batteries (Figure 4).

Figure 4 MHP-TA is small in size
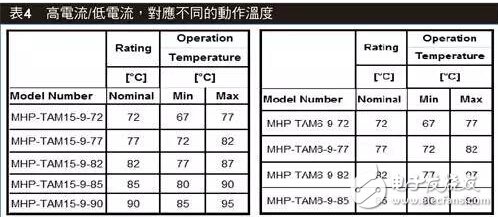
MHP-TA is divided into two series, high current (15A) and low current (6A), corresponding to different operating temperatures, as shown in Table 4.
. Selection of components to consider
MHP-TA has high temperature protection accuracy, small on-resistance, and its performance basically does not change with time and the number of actions. Therefore, MHP is mostly used in lithium batteries that require high temperature protection and performance.
In terms of holding current, low-current specifications of MHP and PPTC have basically the same performance, but in terms of lithium battery cell protection, battery cells with different temperature characteristics and safety performance can choose different operating temperature MHPs, so as to make full use of lithium battery charge and discharge performance , And provide more security protection. When the battery current is required to be high, such as when the requirement is greater than 3.2A at 60 degrees, PPTC is difficult to meet the requirements, and MHP is a better choice, especially the high-current series MHP, which can not only meet the high current demand, but also Effectively protect lithium battery cells (Figure 5).
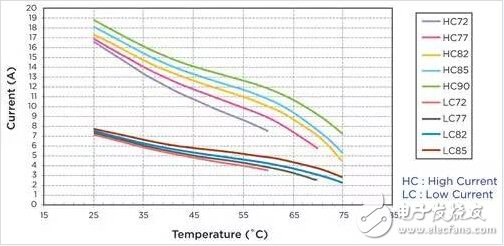
Figure 5 Different temperatures will also affect the safety performance of battery cells
After selecting the MHP specification according to the maximum current requirements of the lithium battery, it must pass the overcharge test, usually 6V/1C, 2C, or 9V, 12V and other specifications. The lower the MHP current and temperature specifications, the better the battery safety protection, but This is in contradiction with the battery current requirements, so it is necessary to take into account these two requirements when choosing; but in some cases it is difficult to meet at the same time, it is necessary to communicate with the customer to strike a balance between the two requirements, such as reducing the battery's high temperature Under the high current requirements, so as to meet the safety requirements.
During the design and assembly of the battery, the MHP-TA cannot be subjected to external forces, and the stress applied to the device or the two terminals will affect the resistance and temperature characteristics of the MHP. The connection method with the battery cell, the degree of fit and the size of the nickel strip will affect whether the battery can pass the safety test (Figure 6).
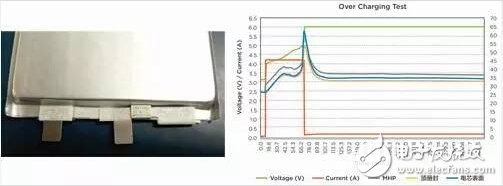
Figure 6 The connection method of MHP-TA and the battery cell, the degree of adhesion and the size of the nickel tape will all affect the safety test.
LPS requires restricted power supply
Almost all mobile phone manufacturers will require lithium batteries to meet the LPS requirements in safety regulations. MHP has the same requirements for LPS and PTC. Under normal circumstances, when the MHP is assembled into the battery, the heat dissipation conditions are not as good as those in the external test, so the actual retention current characteristics of the MHP in the lithium battery will be slightly lower than the current value specified in the specification. Based on the charging characteristics of lithium batteries, the MHP with an operating temperature of 90 degrees can rarely be used for safety protection of lithium batteries, so except for the MHP of 90 degrees, all low-current series MHPs can basically meet LPS. Notebook computers and some tablet computers require higher discharge currents. High-current series MHP can be selected, and other design methods can be used to meet LPS.
Understand the battery design method to choose the right battery cell
In summary, thermal fuse thermal fuse has been less and less used for lithium battery protection due to factors such as large size and manual soldering; surface-mount PPTC is used in mobile phones due to its small size, low cost, and simple reflow soldering process. Battery protection is more and more common, but it is difficult to meet the needs of tablet computers and notebook computers with high current requirements; the protection effect of strip-shaped PPTC is good, so there are still some lithium batteries used, especially square lithium batteries that are more suitable for metal casings. Ion battery assembly; MHP-TA has the performance advantages of high temperature protection accuracy, low on-resistance and stability, so it is widely used in high-end portable electronic products with high safety requirements, especially with high current and high voltage Almost all of the required laptop batteries use this type of product.
The key to meeting the performance requirements of lithium batteries and passing the safety test is not only related to the selection of protection device models and specifications, but also to the specific battery cell types, charge and discharge performance, safety characteristics, connection and installation methods of protection devices, circuit boards and battery assembly. The heat dissipation conditions are closely related. Therefore, in order to provide Fuse/PPTC/MHP-TA samples more accurately and quickly when starting a new battery project, communicate with battery designers as much as possible, and learn as much as possible about battery performance requirements, assembly methods, and safety. Regulatory requirements and detailed manufacturing processes, etc., all help to avoid project delays due to failed tests.
12 Degree Travelator,Passenger Elevator Motor,12 Degree Moving Walkways,Passenger Panoramic Elevator
XI'AN TYPICAL ELEVATOR CO., LTD , https://www.chinaxiantypical.com