0 overview
The PoC (Push to Falk over Cellular) mobile phone intercom service that has received much industry attention has entered the operational stage in China. Ordinary smart phone users who activate this service can talk to one or more mobile phones with the same service function by pressing the PoC function key on the terminal without dialing a long list of phone numbers. The PoC service is more convenient and faster than the traditional mobile phone call. It is a personalized instant messaging service that integrates voice and data.
1 PoC business characteristics
The business characteristics of PoC can be summarized as follows:
(1) Push-to-talk: The user can select individuals or call groups from the address book and press the PoC function key to start the call. The call delay for this service is very short, usually no more than 2 seconds.
(2) Half-duplex communication: Speaking needs to apply for the right to speak, and other people in the talk group can only answer when speaking.
(3) Multiple answering modes: the user can choose manual or automatic answering mode, or set to automatic rejection mode.
(4) Support one-to-one conversations and group conversations: Companies or family members can use this function to communicate similar to conference calls.
(5) Roaming: PoC utilizes the packet switching capability of the IP network, and the service is not restricted by the geographic location, and roaming across the entire network can be achieved.
(6) Presence service: Similar to the interface and functions of instant messaging software, users can set the "call status" (online, incognito or offline), and change the attributes of friends.
(7) Multi-party PoC session: A single PoC terminal can be in multiple PoC sessions simultaneously. PoC has the function of concurrent sessions, and users will not suspend any session.
(8) Access List (Access List) management: support accept member list and reject member list.
(9) Enhanced functions for existing services: In addition to real-time voice communication, PoC can also support text transmission, MMS transmission, and online games between members of the call group.
(10) Low cost overhead: PoC can save a lot of network resources, so the price is low, and online and offline billing separately.
2 IMS architecture
IMS is an open architecture system. 3GPP uses a layered approach to design it. It can separate service and control, call control and media transmission. Its bearer is provided by the underlying transport layer. Business logic is implemented by the application layer. The IMS core system is the middle control layer, which provides session control functions for services.
The important entity structure in the IMS architecture is shown in Figure 1. 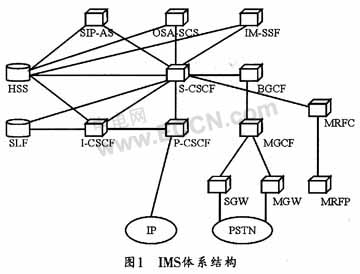
2.1 CSCF function
CSCF (Call Session Control FuncTIon, call session control function) is the core control entity of IMS, which is responsible for processing user multimedia sessions and implementing the softswitch control function. CSCF can be divided into three categories, one is P-CSCF; the other is Z-CSCI; the third is S-CSCF. The P-CSCF (Proxy-CSCF) is the first connection point for the UE (User Equipment) to access the IMS network, and all SIP signaling flows from or to the UE pass through it. The P-CSCF is responsible for session routing, bearer authentication, SIP compression and decompression, IPSec security association, and interaction with policy decision functions.
I-CSCF (InterrogaTIng-CSCF) is located in the home domain and is the entry point from the visited domain to the home domain. It is also the main connection point between IMS and other PLMNs. The I-CSCF is responsible for finding user location information in order to determine the route, and assigns the S-CSCF to the user, and can also hide the internal topology information of the IMS network.
S-CSCF (Scrying-CSCF, serving-CSCF) is in the core control position in the IMS core network. It interacts with HSS and is responsible for handling user registration authentication, making routing decisions, maintaining session state, and charging.
2.2 HSS function
The HSS (Home Subscriber Server, home subscriber server) in the IMS architecture is a central database that stores user-related information. The main data includes user identity, registration information, user authentication, roaming authorization, assigned S-CSCF information, and Business trigger information, etc. The HSS knows the user's current location and the service specified by the user, while the CSCF can ask the HSS for relevant information. For example, I-CSCF can be used to select the most suitable S-CSCF information for the user.
2.3 AS application server
AS (ApplicaTIon Server) is an entity that provides value-added multimedia services and is located in the user's home network or a third-party location. The third party here refers to a network or an independent AS. The main functions of the AS are to handle SIP sessions sent from IMS, initiate SIP requests, and send billing information. AS has a wide range of value-added multimedia services. A multi-service call may require multiple ASs to participate.
2.4 MRF media resource function
MRF (Media Resource FuncTIon, Media Resource Function) is composed of MRFC (MRF Controller, Media Resource Controller) of signaling plane and MRFP (MRF Processor, Media Resource Processor) of media plane. Among them, MRFC handles SIP communication from and to S-CSCF, and controls MRFP; MRFP can provide user resources indicated by MRFC, and complete functions such as media stream mixing and audio code conversion.
2.5 BGCF egress gateway control function
BGCF (Breakout Gateway Control Function, exit gateway control function) is the selected exit point for the called out of the IMS domain or into the CS domain. If the selected outlet is on the same network as this BCBG, a media gateway control function of this network is selected for further call processing; if it is a different network, the BGCF forwards the session to the BGCF of the corresponding network. The IMS networks of different operators can communicate with each other without going through the BGCF.
3 PoC technical solution based on IMS domain
Arranging a certain number of SIP proxy and registration server on the existing 3G network can construct SIP / IP Core (SIP / IP core network) with IMS function, so as to provide PoC with addressing, routing and roaming functions. Such a scheme may be referred to as an "IMS domain-based scheme". This solution is convenient for roaming, good interoperability, and simple transfer between multiple services, which is the direction of future development of multimedia services. The support of IMS to PoC is the support of SIP / IP Core to PoC, which mainly implements the functions of PoC service registration, SIP signaling routing, SIP signaling compression, address resolution, hidden identity management, and charging.
4 PoC architecture
4.1 Main entities of PoC
IMS-based PoC architecture mainly includes PoC client, PoC server, group list manager (XDMS), SIP / IP core network, etc. Figure 2 shows the architecture of PoC. 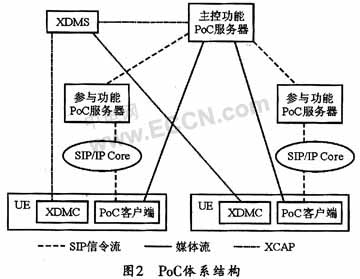
(1) PoC client
Generally, the PoC client is software in the UE (User Equipment) to access people and use PoC services. The main functions of the PoC client include: initiating registration, authentication request, initiating session invitation, participation and termination request, It can generate, send and receive voice bursts (Talk Bursts), and supports the control of voice bursts and the negotiation of TBCP (Talk Burst Control Protocol).
(2) PoC server
The PoC server is an application server in the IMS architecture and is the most important functional entity for implementing PoC services. It is divided into two roles: main control and participation functions.
The functions shared by the two roles include: SIP session processing, protecting user address privacy, supporting user plane adaptation process, supporting TBCP, and transcoding different codecs. The other functions of the master PoC include the mandatory implementation of group participation strategies, providing information to users, providing centralized media distribution, call burst control functions, media quality information and billing reports, etc .; the other functions of participating PoC are mandatory call enforcement Into the PoC session strategy, store PoC client response mode, session blocking and other settings, and provide billing reports.
(3) SIP / IP Core (SIP / IP Core)
SIP / IP Core can replace the standard IMS network, and can realize the functions of the IMS system, including the routing of SIP signaling between the PoC client and server, providing addressing and address resolution, supporting SIP compression, maintaining registration status, according to The configuration of user services authenticates and authorizes PoC clients, and provides billing information and legal interception.
(4) PoC XDMS (PoC XML Document Management Server, PoC document management server)
PoC XDMS is an application configuration setting management server. It stores PoC specific data. The main functions are the creation, modification, reading, and deletion of group lists. It is responsible for the authorization of SIP and XML configuration access protocol requests introduced.
(5) PoC XDMC (PoC XML Document Management Client, PoC document management client)
PoC XDMC can communicate with XDMS and is responsible for creating, modifying, saving and deleting XML leather goods.
4.2 PoC related protocols
PoC session control and other signal transmission are all based on SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), which can be used to create, modify, and terminate the session process participated by one or more participants. It is a text-based request response protocol.
Voice traffic transmission is based on RTP / RTCP (Real Time Real-Time Transmission Protocol / Real-Time Transmission Control Protocol) flow bearing method. As a PoC voice transmission protocol, RTP can transmit voice packets; RTCP can adjudicate the quality of RTP sessions.
XCAP (XML Configuration Access Protocol, XML configuration access protocol) is used to upload customer information to the server. In addition, OMA also defines the TBCP protocol, which can be used to implement the distribution of PoC media streams and control of the right to speak.
5 PoC business process
5.1 PoC registration process
There are four steps to the PoC registration process. The first is that the client sends a REGISTER request carrying relevant registration information (public user ID, private user ID, home network domain name, UE IP address, etc.) to the P-CSCF;
The second is that after receiving the registration request, the P-CSCF checks the originating domain name of the initiator to find the population point I-CSCF of its home network, and forwards the REGISTER request message to this I-CSCF;
Next is the I-CSCFNHSS query whether the user is allowed to register, if allowed, the HSS will return the selected S-CSCF to the I-CSCF;
Finally, the I-CSCF forwards the registration message to the S-CSCF, and then after authentication, the S-CSCF downloads the relevant information of the user from the HSS, and then returns 200 OK, so that the registration process is all over.
5.2 PoC session establishment process
PoC sessions are half-duplex voice services implemented using VoIP technology. When one person speaks, others in the talk group can only listen. Two terminal devices on both sides of the call share a channel for calling and answering. The channel is occupied when the user speaks, and only the channel is monitored when answering. Figure 3 shows the flow chart of the main PoC entities during the session. The establishment of its process can be carried out as follows: 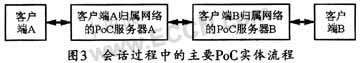
Step 1: User A selects user B who needs to call from the address book, and presses the PoC call function key on the client. Thereby triggering client A to send a SIP invite (SIP Invite) request to PoC server A of its home network;
Step 2: Server A generates a new SIP request and sends it to user B. After being intercepted by the PoC server of user B's home network, it will query whether user A is in user B's call rejection list or auto answer list;
Step 3: Assuming that user A is in the automatic answer list of user B, PoC server B sends a SIP Invite request to client B, and returns a SIP session processing response to server A;
Step 4: When server A receives this message, it indicates that user B is willing to make a call connection, so it will send a SIP202 acceptance response to user A, and at the same time allocate a communication channel to user A, user A ’s mobile phone sends Prompt tone
Step 5: User A can start talking when the conversation channel has not been established end-to-end. This is a communication mode called pre-media processing. In this way, the PoC server must buffer the conversation audio stream until the end of step 7;
Step 6: Since the client B adopts the automatic answering mode, it sends a SIP 200 OK back to the server B to indicate tacit approval;
Step 7: Client A receives the SIP notification (OK) message, indicating that the call channel has been established, and the channel call right is really given to user A;
Step 8: User A obtains the right to talk and starts speaking, the PoC system transmits the media stream for user A;
Step 9: When user A stops speaking and releases the PoC function key on the client to release the call right, the call right is idle;
Step 10: User B presses the PoC call function key on the client to initiate a call request and obtain the call right;
Step 11: User A obtains the right to talk and starts speaking, and the PoC system transmits the media stream for user B;
Step 12: After user B releases the PoC function key, the call right returns to the idle state again;
Step 13: If there is no further call requirement between users, there is no need to manually end the call connection. After the system exceeds a certain time interval, the PoC server will automatically send a SIP BYE message to end the call.
6 Conclusion
IMS is undoubtedly a very powerful architectural system. Its basic functions (such as signaling and routing) will make service deployment and application expansion easier and easier. The PoC service is a new value-added point for 3G. With the gradual improvement of its standards, it will inevitably shorten the call delay, further improve the call quality and interconnectivity, and bring more abundant and convenient services to 3G users .
This Automation curtain is specially designed for automation industry. SDKELI LSC2 light curtain is designed for automation field, with small size, compact structure and strong anti-interference ability, and the product meets IEC 61496-2 standards. The automatic light curtain is with reliable quality and very competitive price. It has been used in many factories and has replaced curtains from Sick, Omron, Banner, Keyence, etc.
Automatic Light Curtain,Laser Light Curtain,Automation Light Beam Sensor,Automatic Infrared Beam Sensor,Infrared Beam Curttain Sensor,Infrared Beam Sensor
Jining KeLi Photoelectronic Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdkelien.com