This article describes how to use advanced test platforms to test certain key parameters of ADSL chips, so that semiconductor manufacturers can reduce the cost of ADSL device testing.
ADSL is a modem technology that fully utilizes the unused resource capacity of ordinary telephone twisted pairs. It adopts asymmetric transmission mode, and the downlink speed from the central office (CO) to the remote end (RT) can reach up to 4 times the uplink speed. . This asymmetric performance is ideal for market-oriented consumer broadband applications such as video and Internet access, because in these applications the downstream data rate must be very high, while the upstream data from the user to the central office (CO) Generally less. This usage model also applies to business communications from company servers to employees, partners, and customers.
Unlike analog modems, ADSL modems do not enter the public switched telephone network (PSTN), while using advanced modulation technology, the signal frequency and data rate sent by them are much higher than analog modems. ADSL supports a downlink rate of up to 8Mbps and an uplink rate of up to 832kbps. However, as the signal transmission distance increases, the data transmission rate using this technology will also quickly decline. For example, when the distance between the user end and the office end is less than 12,000 feet, the ADSL rate can be maintained at 8Mbps, and when the distance is increased to 18,000 feet, the rate can only reach 1.5Mbps.
ADSL uses the familiar frequency division multiplexing (FDM) method to provide broadband services, while supporting traditional "ordinary telephone service" (POTS) networks. The FDM method used by ADSL is mainly discrete multitone (DMT) modulation. The DMT modulation method divides the approximately 1.1MHz frequency spectrum into 256 equally spaced sub-channels or tones, with each sub-channel occupying 5.3125KHz. In the DMT spectrum, each channel works as an independent channel, and uses quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) modulation method to encode digital information.
In addition to data transmission, these channels can also be used for independent network management or performance testing. Lower frequency channels are not used to transmit signals, and are generally reserved as protection bandwidth to avoid interference with traditional POTS equipment at the lower end of the spectrum. In the frequency bands immediately above and above these protection channel frequencies, a small number of channels for uplink data transmission are allocated, and the remaining higher frequency channels are used for downlink data transmission. Just like other modem technologies such as V.32 and V.34 modems, ADSL modems also need to use echo cancellation technology to solve the problem of overlapping upstream and downstream channels. And to provide telephone and data services at the same time must rely on low-pass filters or splitters to achieve separation.
testing method
In order to improve the cost-effectiveness of ADSL, manufacturers need to provide equipment that can extend the distance between the central office and the customer premises, which can reduce the number of terminal points, thereby reducing the cost of laying fan-shaped subscriber lines. In addition, the coverage performance of ADSL equipment is one of the most competitive factors. Longer telephone lines will cause up to 90dB of attenuation in the high-end band signals used by ADSL. Therefore, semiconductor manufacturers usually use analog-to-digital converters (ADC) and digital-to-analog converters (DAC) with higher dynamic range and lower noise specifications in the design of ADSL equipment.
In ADSL modems, the noise and linear performance of the analog front end (AFE) is the key to the ADSL modem's ability to obtain the ideal data rate over longer cables. Not-too-noisy noise and linear design margins often increase the challenge of testing, because manufacturers need to provide ADSL test instruments with a wider dynamic range and higher accuracy. In short, the test cost should be less than or at least equal to the previous generation of low-performance ADSL The cost of testing equipment.
Manufacturers can use the single-tone test method to determine the pure dynamic range, standard distortion and noise floor level of ADSL. This direct test method is sufficient to quickly find various defects. The single tone test method is more effective for the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the test equipment. Although the linearity specifications of ADSL converters are strict, SNR is still an important device parameter necessary to ensure the correct operation of ADSL. The single-tone test also measures the overall harmonic distortion (THD) and distortion-free dynamic range (SFDR) of the device.
After calculating the SNR, these basic dynamic linear tests only require a small amount of additional processing, so this test basically does not spend too much test time overhead. That is to say, the test time requirement of the tone test is very moderate relative to its efficiency. In addition, many industry-leading test systems provide pre-made routines to facilitate the development of these tone tests. Since the single tone test method can test multiple key parameters using a set of data, most defective devices fail the single tone test.
Although static linear test is the traditional content of ADC specification, it is not suitable for equipment evaluation for ADSL equipment. ADSL ADC's high conversion rate is usually offset by high resolution. At this time, a large amount of data needs to be captured, thereby consuming a large amount of DSP operation time. Another factor that needs to be considered is the high-frequency signal used in ADSL equipment. The static linear test will be very different from the dynamic response of the device.
Comparing various tests of this type of device, it can be found that the most practical effect is still the basic loopback test. The engineer connects the transmitter to the receiver and checks whether the encoded data sent from the output can be decoded correctly at the input. Although this highly practical test method does not provide the information necessary to isolate faulty equipment in complex designs, it is very fast to execute and has the lowest cost.
Uv Disinfection Lamp, 36W 110V Ultraviolet Sterilizer, Air Purifier with Ozone Remote Control Timing, UV-C Disinfection light for Home, Kitchen, Bedroom,School,Office and Hospital.
Need to change the sterilization lamp frequently, UV sterilization lamp has a slow leak phenomenon. After 8000 hours of use, the lamp needs to be replaced in time, usually once a year.
[Excellent material] Made of high transmittance quartz glass material, obvious sterilization effect. Lamp life 8000 hours, It removes odors, dust particles and germs which can cause allergies, asthma and other harmful maladies.[High Efficiency] Disinfection lamp UV germicidal help solve the problem of disinfection home life. effectively covers up to 40 Square meter. disinfect surface, Round 360° Thorough cleans.
[Multifunction] Disinfection Lamp UV germicidal help solve the problem of disinfection home life. suitable for many occasions small space like car, bedroom, kitchen, shoes cabinet, washing room, baby's room, pet house, toilet, much more space you desire to purify.
[Easy to clean] When cleaning the UV lamp, cut off the power and use a clean, soft cloth or alcohol graze hanged gasoline and other organic solution to wipe.
How effective is UV sterilization?
The use of UV sterilization, or ultraviolet germicidal irradiation, has been found to be extremely effective. Sources of UV sterilization can kill over 99% of viruses, bacteria, and fungi in an extremely short amount of time.
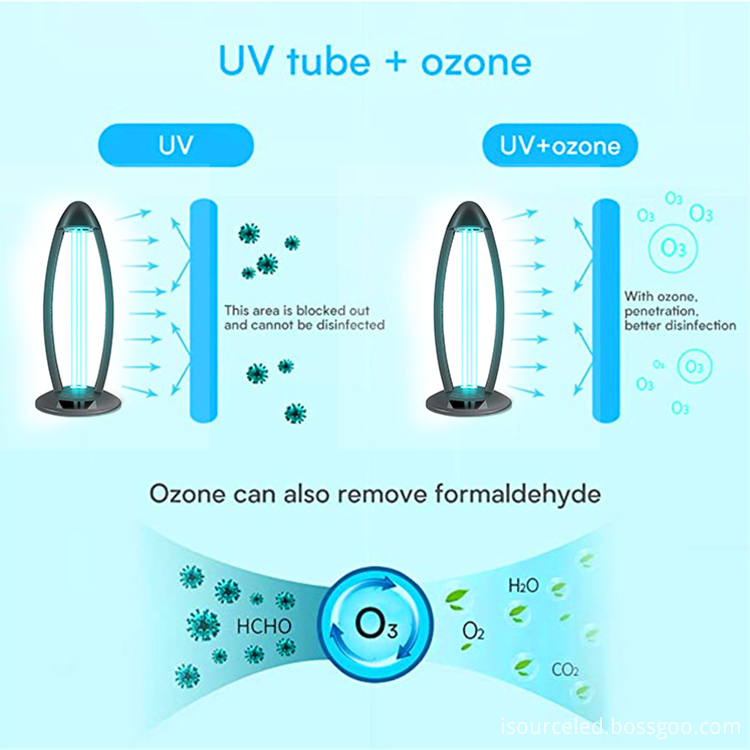
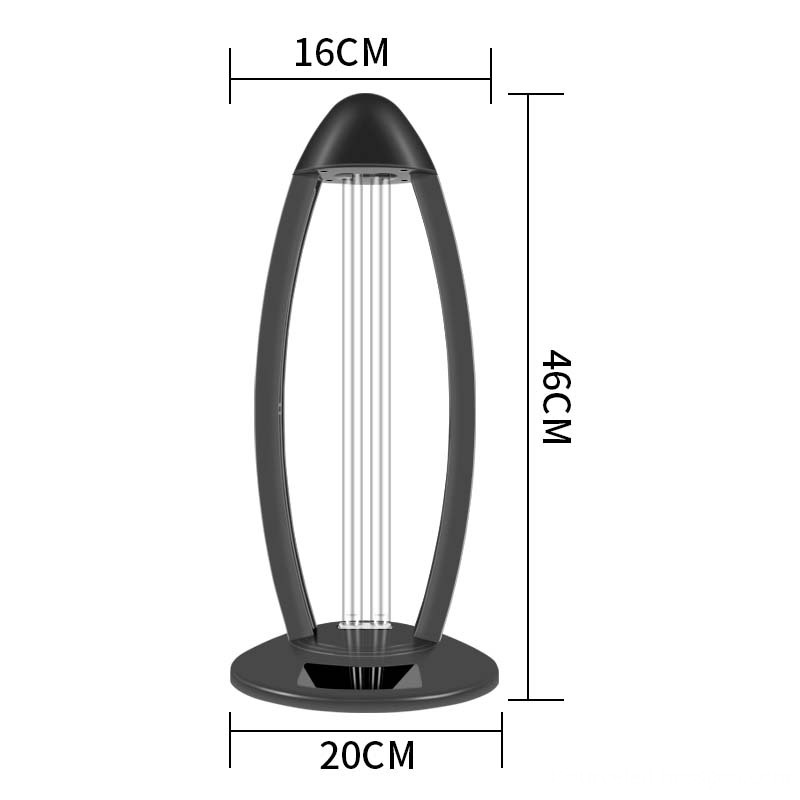
Uv Disinfection Lamp
Uv Disinfection Lamp, 36w Uv Disinfection Lamp, ozone Uv Disinfection Lamp, 254nm Uv Disinfection Lamp
Shenzhen Dianjiang Engineering Co. LTD , https://www.isourceled.com