The current reference standards for laser welding are not uniform. For processing with a higher degree of automation in the automotive industry, the establishment of a unified process standard is conducive to the promotion of equipment. The analysis at the back of the article summarizes the common defects of laser welding and gives solutions.
1. Foreign laser welding automobile standardsAbout Volkswagen's laser welding standards
1. Refer to DIN 18800 Part7, SecTIon3.4, or DVS Code of PracTIce 0705, SecTIon3.2 for sheet requirements. Suitable for carbon steel plate thickness 0.5~3.0mm, the plate structure bears static load. Plates include weld joint types and material types (refer to DIN EN ISO13919-1)
2. Laser welding welds are subject to some mandatory inspections in accordance with the requirements. The external dimensions of the weld cross-section refer to DIN 32511, which mainly include the reinforcement, penetration, penetration width, welding depth, sheet thickness, etc., see Figure 1.
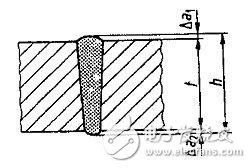
Figure 1 Cross-sectional dimensions of laser welding
3. Laser welding requirements
With reference to DVS 3203 Part 3, the materials are divided into cold rolled steel plates (DIN 1623 Part 1, EN10027), rolled steel strips (DIN 1624, EN 10027), hot rolled steel plates (C<0.20%, TL 1111), and cold rolled narrow strips For plates (refer to DIN 17100, ie EN 10027), for the carbon content of the steel plate greater than 0.22%, or the thickness of the zinc layer greater than 7.5um, you need to consult an engineer.
4. Weld design
The weldability of welds mainly considers three factors: design, material and production. The main design characteristics of the weld include load characteristics, weld parameters, clamping, tolerance of the workpiece, post-weld treatment, etc., see DIN 8528 Part 1.
4.1 Design layout (see DVS 3203-4)
Mainly consider the joint type (butt joint, corner joint, lap joint, stitch welding, crimping, etc.), weld type (including position and other information). If it is galvanized sheet, the flat plate butt gap is controlled within 0.05~0.1mm, and the fillet weld is single The side angle is greater than 10°.
4.2 Process and quality assurance
For weld quality, refer to EN 729 Part 1, and for comprehensive quality requirements, refer to EN 729 Part 2.
When there is no clear description, please refer to the general standards EN 25817 and En ISO 13919-1, which generally meet the requirements of Class B.
Evaluation criteria: Refer to EN 970 for external defects or forming standards, just use a five-fold magnifying glass to observe the weld forming.
Destructive test: as shown in the figure, the lack of fusion is one of the welding defects.
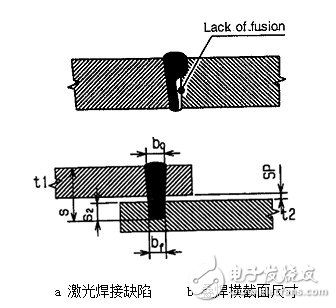
a Laser welding defect b Cross section size of overlap welding
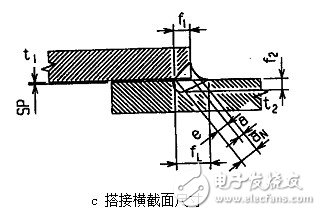
c lap cross section size
Figure 2 Cross-sectional dimensions of laser welding
Please refer to En 22553 for welding seam drawings. The markings and corresponding codes of welding methods should be one-to-one correspondence.
2. Laser welding seam defects and their causes and countermeasures:1. Welding spatter: After laser welding is completed, many metal particles appear on the surface of the material or workpiece, which adhere to the surface of the material or workpiece.
Reason: The surface of the material or workpiece is not cleaned, there are oil stains or contaminants, or it may be caused by the volatilization of the galvanized layer.
Countermeasure: Clean the material or workpiece before laser welding.
2. Welding seam accumulation: There is obviously too much welding seam filling material during filling welding, and the welding seam is too high.
Reason: The wire feeding speed is too fast or the welding speed is too slow during welding.
Countermeasures: increase the welding speed or reduce the wire feed speed, or reduce the laser power.
3. Welding deviation: the weld metal is not solidified in the center of the joint structure.
Reason: Inaccurate positioning during welding, or inaccurate alignment between filling welding time and wire.
Countermeasures: Adjust the welding position, or adjust the position of the filler welding time and wire, and the position of the light, wire and weld.
4. Weld depression: the phenomenon of depression on the surface of the weld metal.
Reason: During brazing, the center of the welding spot is poor. The center of the spot is close to the lower plate and deviates from the center of the weld, causing part of the base metal to melt.
Countermeasures: adjust the light and silk matching.
5. Interruption of the weld or uneven thickness: When the weld is brazed, the weld is interrupted or uneven in thickness without wire feeding.
Reason: Unstable wire feeding, or discontinuous light output, etc.
Countermeasure: Adjust the stability of the equipment.
6. Porosity: Porosity appears on the surface of the weld.
Reason: The surface of the weld is not cleaned, or the zinc vapor of the galvanized sheet is volatilized.
Countermeasures: clean the surface of the weld and improve the volatilization of zinc when heated.
7. Welding: When the weld track changes greatly, it is easy to appear welded or uneven forming at the corners.
Reason: The welding seam trajectory changes greatly and the teaching is uneven.
Countermeasure: Weld under the optimal parameters, and adjust the teaching so as to coherently excessive corners.
Antenk offers flat cables from its own production – the location of the in-house Flat cable production is the antenk factory in shenzhen,Made in China. The FLAT CABLES are produced with latest state of the art production facilities and fulfill the Automotive standards.
Flat cable is a standard organization and is suitable for mobile electrical equipment with AC rated voltage of 450v/70v and below. Flat structure is especially suitable for frequent bending occasions, without kinking and folding neatly, such as driving. Yb, YBF and YBZ products can meet the needs of various occasions. It is suitable for the electrical connection between mobile electrical equipment in the harsh environment of power generation, metallurgy, chemical industry, port and so on.
Flat Cable
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkelec.com