First of all, let's look at what should be paid attention to when measuring power with an oscilloscope.
1, try to expand the measurement dynamic range1) Increase the measurement resolution by calculating the average value
2) Improve measurement resolution with high resolution acquisition
3) Use AC coupling to remove DC offset
4) Limit bandwidth with oscilloscopes and probes
2. Select a detection method to optimize signal integrity5) Use differential probes for safe and accurate floating measurements
6) Do not select the detection accessory that couples the radiated power
7) Select the probe that avoids the most sensitive setting of the oscilloscope
3, using the oscilloscope to calculate powerDescribes how to use the power analysis software package on the Teledyne LeCroyHDO6000 oscilloscope to obtain power values ​​without the need to do the right mathematical calculations.
Both analog and digital oscilloscopes are voltage responsive instruments. The current is measured with a suitable conversion circuit, usually with a current probe or a resistive shunt circuit. The oscilloscope display shows an instantaneous function of voltage or current versus time. The product of these two values ​​is the instantaneous power.
Figure 1 shows a basic line power measurement.
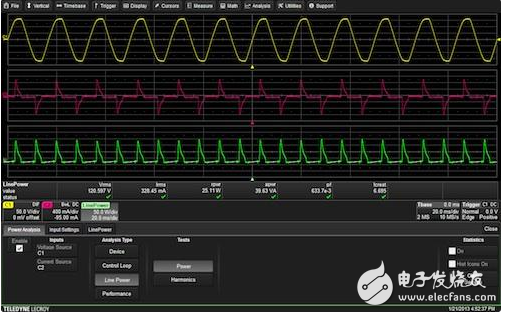
Figure 1: Power measurement components (instantaneous voltage, current, and power) displayed on an HDO6000 oscilloscope configured with power analysis. Active power and apparent power are automatically calculated and displayed.
The product of the instantaneous voltage (channel 1) and current (channel 2) is the instantaneous power, as shown by the line power trace at the bottom of the figure. Note that the power waveform contains a waveform that is twice the current or voltage frequency and has a DC offset. This DC offset represents the average power delivered to the load. The average power or active power is indicated by the symbol P and the unit of measurement is watts (W). In Figure 1, the active power is automatically determined by determining the average of the instantaneous power waveforms. In this example, the active power is shown as the parameter rpwr, which has a value of 25.11W.
The product of the effective (rms) current and the effective (rms) voltage is called the apparent power. The apparent power is indicated by the symbol S, and the unit of measurement is volt-amperes (VA). In the above example, the apparent power is equal to:
S=120.59*0.328=39.6VA
The apparent power is automatically calculated and displayed with the parameter awrr. For resistive loads, the apparent power and average power are equal.
The ratio of average power to apparent power is the power factor. In the case of a sinusoidal signal, the power factor is equal to the cosine of the phase angle between the current and voltage waveforms. The calculation of power factor is more commonly the ratio of active power to apparent power. In this example, the power factor is also automatically calculated and displayed, using the parameter pf. The power factor value is 0.633.
Icrest is the crest factor of the current waveform. The crest factor is the ratio of the peak-to-peak current to the effective value.
The reactive power N can be calculated by substituting the active power and the apparent power using the following formula:
N=(S2-P2)1/2
The unit of reactive power is volt-ampere reactive or VAR. Most users are interested in active power and power factor, so reactive power is not automatically calculated.
4, the secret of using the oscilloscope to perform power measurement seven secret tips: improve the measurement resolution by calculating the average valueIn some power measurement applications, you need to measure the value of a large dynamic range while also requiring fine resolution to measure small changes in parameters. In addition to high-resolution digitizers, you can use other acquisition methods to reduce random noise and increase the effective dynamic range of the measurement, such as averaging and high-resolution acquisition.
The averaging method requires that the signal under test must be a repetitive signal. The algorithm averages the points acquired multiple times during each period. This reduces random noise and gives you a higher vertical resolution. How many averages do you need to calculate for each additional vertical resolution? The answer is that each time you calculate the average of 4 samples, you can increase the vertical resolution by one bit. The principle is as follows:
– increased number of bits = 0.5 log 2 N
–N=Number of samples for calculating the average
– For example, averaging 16 samples, the vertical resolution will increase:
– Number of digits = 0.5 log 216 = 2
– Therefore, the effective vertical resolution is 8+2=10 bits.
This algorithm can increase the vertical resolution up to 12 bits, because other factors, such as the oscilloscope's vertical gain or offset accuracy, will play a decisive role. The advantage of the average mode is that there is no limit to the real-time bandwidth of the oscilloscope. The disadvantage is that it only applies to repetitive signals and reduces the rate of waveform update.
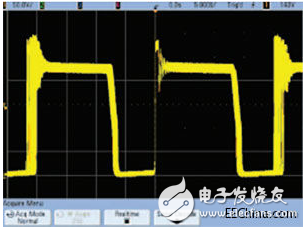
Figure 1. Switching Power Supply Vds captured in normal acquisition mode
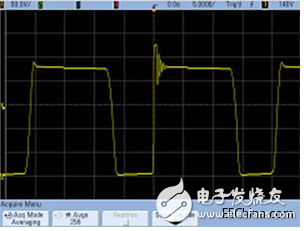
Figure 2. Vds captured in normal averaging mode
Power 30W ,output voltage 3-12V, output current Max 1.2A , USB output 5v 2a, 6 dc tips. We can meet your specific requirement of the products, like label design. The material of this product is PC+ABS. All condition of our product is 100% brand new.
Our products built with input/output overvoltage protection, input/output overcurrent protection, over temperature protection, over power protection and short circuit protection. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
30W Wall Adapter ,30W Wall Power Supply,30W Power Cord In Wall, 30W Wall Power Adapter
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.laptopsasdapter.com