The optical communication device is the core foundation of the optical communication system and is an important component of the optical transmission system. Its technology is a forward-looking, pilot, and exploratory strategy in the optical communication field. The technology represents a country in optical communication. The level of competence in the field. This article first introduced the development history of China's optical communication devices and the status quo of China's optical device technologies and industries. Second, it described the challenges faced by China's optical communication devices. Finally, it introduced the development trend of optical communication devices and the development of optical communication devices in China. Suggestions, specific follow Xiaobian together to find out.

Optical devices are divided into active devices and passive devices. Optical active devices are key components of the optical communication systems that convert electrical signals into optical signals or convert optical signals into electrical signals. They are the heart of optical transmission systems and include semiconductor light-emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes (LDs), Photodiodes (PINs), avalanche photodiodes (APDs), erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs), Raman amplifiers, and modulators. Optical passive devices are devices that consume a certain amount of energy in an optical communication system but do not have photoelectric or electro-optical conversion. They are key nodes of optical transmission systems and mainly include optical fiber connectors, couplers, wavelength division multiplexers, optical switches, and optical devices. Attenuator and optical isolator.
1) History of Optical Active Devices
Research on China's optically active devices began in the 1970s. At that time, western countries imposed high-tech blockades and embargoes on China in accordance with the so-called “Batumi†regulations. Therefore, the Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan Institute of Posts and Telecommunications, and the 44th Research Institute and 13th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group, Self-reliant, developed a short-wavelength laser with a wavelength of 850 nm. Since then, these units have developed long-wavelength lasers with wavelengths of 1310 and 1550 nm, which meet the needs of China's optical communications at the beginning stage.
Prior to 1993, the optical active components required for China's optical communications were basically provided by domestic manufacturers. As a result, Western countries recognized the use of "Batum" regulations in active devices and other areas, and imposed technical embargoes and embargoes on China. On the contrary, it will lose China's huge market, and it will not be worth the candle. Therefore, the “Batum†regulation has to be declared ineffective, and overseas optical active devices begin to flood the Chinese market.
With the rapid development of optical communication technologies, the technical requirements for optical active devices have become higher and higher. Although Chinese authorities have made great efforts to track the world trend and achieved breakthroughs in quantum well semiconductor materials and device technology, the level of laboratories for advanced devices such as distributed feedback (DFB) semiconductor lasers has also greatly improved, but due to the input of human resources. Far from material resources, the gap with the international advanced level has widened.
At present, only a few units in China can independently manufacture lasers and detector dies, and they are limited to dies with rates below 10 Gbit/s. The high-rate dies, unit devices and erbium-doped fibers required for China's optical communication equipment and systems all need to be imported. Most active device companies purchase foreign dies as devices, purchase foreign devices as modules, and purchase erbium-doped optical fibers from abroad. Amplifier assembly, optical communication equipment company to buy foreign modules to do the system.
2) The history of the development of optical passive devices
The study of optical passive devices in China started with the advent of optical fiber technology in the late 1970s. At the time, the connection of optical fibers was one of the six major issues that must be resolved in optical fiber communications. In addition, problems such as shunting, switching, and wavelength multiplexing must be resolved. As a result, the 23rd Institute of China Electronics Technology Group, the Solid State Devices Research Institute of Wuhan Institute of Posts and Telecommunications (now Wuhan Optical Information Technology Co., Ltd.) and the 34th Institute of China Electronics Technology Group have started from scratch and are committed to all-fiber structures and Research on the combination of micro-optical discrete components, development of multi-mode optical fiber connectors, splicing type and fusion taper type optical couplers and mechanical optical switches and other products, to meet the short-wavelength and long-wavelength multi-mode optical fiber communication research at that time demand.
Since then, optical communications have entered the single-mode long-wavelength phase and started to be used in large numbers. As optical passive devices are not only more technically demanding, they are also increasing in number and are urgently required for industrialization. In the aspect of optical connectors, the optical centering cutting APT connector production line was first introduced to meet the needs of the initial stage of domestic single-mode optical communication development. Afterwards, with the success of mass production technology of ceramic casing, the quality of the optical connector has been further improved, and it is easy to assemble. Therefore, there are many companies that have assembled connectors for parts production. In the area of ​​fiber couplers, the introduction of microcomputer-controlled fusion taper devices has made coupler production simpler; more gratifyingly, through theoretical research and practical exploration, various broadband products can be produced on the same equipment. Couplers and dual-wavelength wavelength division multiplexers have excellent product performance, thus forming an optocoupler industry. At present, most of the optical connectors and optocouplers used in China's optical communication systems are domestically produced.
At the time, the industry that appeared to be an optical passive device at first appeared to be developing faster than an optically active device, but behind this glory there were still some problems. Ceramic blanks such as fiber optic connectors also need to be imported, and the proprietary intellectual property rights of fiber optic connector technology are almost zero. By the end of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century, with the development of fiber access networks, dense wavelength division multiplexing systems, and all-optical communication networks, existing optical passive devices that can be mass-produced cannot fully meet the needs. For example, a high fiber density patch panel requires a small-sized optical fiber connector, a fused-tapered device cannot produce a dense wavelength division multiplexer, and a conventional small port number of optical switches cannot cascade to form a large number of port matrix optical switches. These problems force people to stay in the production and competition of low-end products, and must develop high-end optical passive devices to meet the needs of the development of optical fiber communications. In response to these problems, some organizations have worked hard, such as the introduction of assembly jigs for small optical connectors, and the use of micro-optical device structures to develop dense wavelength division multiplexers that can multiplex several or even more than a dozen lines. However, in order to solve the matrix optical switch problem of several tens of wavelength division multiplexing and large port numbers, only photonic integrated devices can be used. At present, the gap between the level of passive devices in China and foreign countries is not big, even reaching the international advanced level.

China attaches great importance to the research and development of optical communication devices, arranges special topics through national high-tech development plans, organizes technological research, and follows international advanced technology and other measures, which has greatly promoted the research and development and industrialization of optical communication devices. From the country to the provincial and municipal governments at all levels to fully mobilize all kinds of resources, and actively create a good development environment and conditions, in the field of technology development and product development, Chinese companies have mastered a large number of key technologies, some projects have been close to research and development capabilities At the international advanced level, high-end optical communication device technologies and products with independent intellectual property rights have been widely used in optical networks. The optical device industry has gradually shifted to China, and China has become an important production and sales base for global optical devices. However, there is still a big gap between the industrial chain structure and the overall level of the industry and the international advanced level. China lags far behind Europe, the United States, Japan and other countries in the field of optical devices. Among the top 10 optical device suppliers, Wuhan Optical Technology Co., Ltd. ranks only fifth in the world, only accounting for a global market share of 5 % (Figure 5), the market share of other Chinese manufacturers is very small, the vast majority is less than 1%. Faced with the Chinese market, which has the world’s largest optical communications market, the most complete industrial chain, and high-quality optical system equipment manufacturers, such market share is clearly inconsistent.
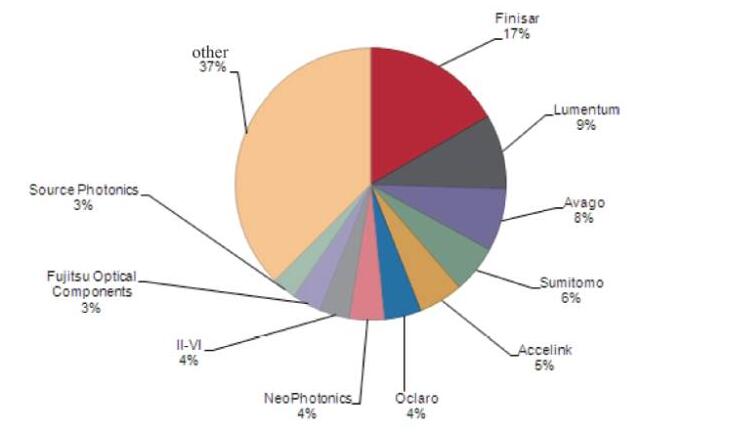
Figure 5 2015 global optoelectronic device company rankings
In terms of basic theoretical research on communication optoelectronic devices, there is not much difference between China and foreign advanced levels. However, the quality of key process technologies and the weak platform of equipment conditions are the “bottleneck†restricting the research and development and sustainable development of China’s telecommunication optoelectronic devices, breakthroughs in the key technologies of related devices, and the ability to research and innovate device technologies. There is a certain gap between the level of key equipment and conditions in the process technology research and the international advanced level.
Although China’s basic theoretical research and basic processes for communication optoelectronic materials, chips, and integration technologies are more fully developed in institutions of higher learning and some specialized research institutes, but also due to limitations in the level of process technology and equipment conditions, some basic theories The process research and practical application are seriously out of touch, lacking sufficient pertinence and practical guidance significance, leading to many frontier research results in the country, and the contradiction between achievement transformation and promotion and application is very prominent. The “empty core†problem of China’s communication optoelectronic devices is very serious. serious. And compared with the advanced level in foreign countries, there has been a dangerous trend of increasing disparities in recent years.
High demand in the optical communications market has also brought demand for upstream chip products. Optical communication chips in the Chinese market rely mainly on suppliers from other countries. At present, a small number of Chinese companies have made breakthroughs in the field of chips. Wuhan Fast Motion Technology Co., Ltd. and Henan Shijia Photonic Technology Co., Ltd. can provide commercial passive AWG and Splitter chips; Wuhan Fast Motion Technology Co., Ltd. and Hisense Group Co., Ltd. The company and HCL Zhengyuan Photonics Technology Co., Ltd. can produce active chips below 10 Gbit/s, but 25 Gbit/s active chips, including VCSEL, DFB, EML, PIN, and APD, all rely on imports. Equipment manufacturers such as Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation and some leading optical device companies are also developing chips. China has made certain breakthroughs in the field of chips, but it has not yet reached a scale, mainly low-end chips. Since optical communication chips are mainly dependent on imports, China's optical device companies have a large profit margin while market demand is rising. Chips have become a constraint factor for the competitiveness of downstream companies. The future development of China's optical communications chip industry may come from downstream optical devices and system companies to extend upstream development, vertical integration, and development of chips. In the case that the upstream chip and the downstream system equipment are relatively concentrated, the optical component manufacturers have a strong incentive to expand upstream, and some strong optical component manufacturers will make breakthroughs in the upstream.
China's optoelectronic device companies have few high-end core technologies with independent intellectual property rights, large dependence on foreign chips and special materials, few products with core competitiveness, overall corporate strength is still weak, and product structure is not reasonable enough. Qualitative seriously, the products provided are also concentrated in the low-end, product added value is not high, the international market competitiveness and profitability have yet to be improved. Although some device manufacturers have a certain scale of production, the technical and technological foundations for sustainable industrial development are relatively weak, and many companies have to rely on vicious price competition in low-end products and low labor costs to survive hard. And gradually become an OEM factory that lacks core technology, has no independent brand, and works for companies in other countries. In the aspect of high-speed products such as active optical devices and 100 Gbit/s optical modules with higher technological content and higher added value such as 10 Gbit/s, the core technology is missing, the commercialization process is slow, and the material growth and die are truly available. There are only a handful of companies that produce a full set of process lines and vertical integration capabilities from chips to devices to modules. The weakness of the upstream materials and chips has led to restrictions on the development of the corresponding optical devices, components and modules. The procurement channels are controlled by countries such as Japan and the United States. In addition, some internationally renowned optical devices and chip companies have shifted R&D, production, packaging, testing, and sales to China in order to reduce costs and grasp China's rapidly growing market demand, further squeezing the market space of Chinese companies[6].
As for high-end optical device technologies, they are basically in the hands of foreign manufacturers. Although China's optical communications companies are also strengthening R&D investment in this area, the gap between them and the international mainstream device vendors is still large. The 100G high-end device is almost entirely dependent on imports, including an integrated tunable laser assembly (ITLA), an integrated coherent transmitter (ICT), an integrated coherent receiver (ICR), and a 100-G customer-side device. Colorless/non-directional/non-blocking reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer CDC ROADM (colorless/direcTIonless/contenTIonless reconfigurable opTIcal add/dropmulTIplexer), wavelength selective switch (WSS), optical cross-connection for intelligent optical networks The connection equipment OXC (optical cross connect) is also mainly dependent on imports. The lack of high-end technologies and products in China has also led directly to China's optical fiber communications equipment manufacturers (such as Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, and FiberHome etc.), and has had to rely on a large number of imported high-end devices to build system equipment, which severely restricts these. The international competitiveness of equipment companies in related fields has affected their further advancement and rapid development in the international market.
In short, the high-end core devices required by China's optical communications equipment manufacturers are almost entirely dependent on imports from the United States, Japan, and Europe; the high-speed optoelectronic chips required for high-end optoelectronic devices are also almost entirely dependent on imports, and are subject to control from chip suppliers in other countries. As the core of the optical communications industry, the growth of basic chips and device suppliers has a bearing on the overall competitiveness of China's optical communications industry, and has become a key bottleneck restricting the long-term development of China's optical communications.

1. There is a big gap between the key process technology capabilities and the level of the process platform compared with foreign countries
In the basic theoretical research of communication optoelectronic devices, there is not much difference between our country and foreign advanced level. However, the quality of key process technologies and the weakness of the equipment condition platform are the “bottleneck†restricting the research and development and sustainable development of China's telecommunication optoelectronic devices. We have breakthroughs in the key technologies of related devices, and we have mastered the capabilities, research and innovation of device technology. There is a large gap between foreign countries in terms of capacity, technological equipment, and key equipment conditions. Although China's basic theoretical research and basic processes for the communication of optoelectronic materials, chips, and integration technologies have been carried out adequately in universities and some specialized research institutes, but also due to limitations in the level of process technology and equipment conditions, some basic theoretical and technological The research and practical application are seriously out of touch, lacking sufficient pertinence and practical guidance. The contradiction that leads to many frontier research results in the country and the transformation and promotion of the application of the results is very prominent. The problem of "hollowing out" of China's communications optoelectronic devices is very serious. And compared with the advanced level in foreign countries, there has been a dangerous trend of increasing disparities in recent years.
2. The gap between high-end optoelectronic devices has become increasingly apparent
China’s telecommunications and optoelectronic device companies have few high-end core technologies with independent intellectual property rights, large dependence on foreign chips and special materials, few products with core competitiveness, and the products provided are also concentrated in the low-end and high-end markets. The added value of products is not high, and the competitiveness and profitability of the international market have yet to be improved. Although some device manufacturers have a certain scale of production, the technical and technological foundations for sustainable industrial development are weak, and many companies have to rely on the low-end The vicious price competition in products and low labor costs have struggling to survive, and have gradually become an OEM factory that lacks core technologies, has no independent brand, and works for foreign companies. With JDSU, Oplink and other well-funded foreign device companies setting up camps in China, the competition for talents has become increasingly fierce. Domestic related companies are facing severe challenges in the continuous loss of outstanding technical talents. The lack of high-end technologies and products in the country has directly led to many domestic manufacturers of fiber optic communications equipment (such as Huawei, Fiberhome, and ZTE) that have considerable influence and status on the international market. They have to rely on a large number of imported high-end devices to build system equipment. This severely restricts the international competitiveness of these equipment companies in related fields and affects their further promotion and rapid development in the international market.
Optical communication device development trendOptical Integration Technology (PIC) is the mainstream development direction of optical devices in the future and has been the focus of attention and research in the industry in recent years. Photonic integrated technology has obvious advantages in terms of size, power consumption, cost, reliability, etc., compared with discrete components currently widely used, and is the mainstream development direction of optical devices in the future.
In recent years, with the gradual accumulation of technology and rising industrial demand, PIC has entered a period of rapid development. Small- and medium-scale PICs have matured and have been widely used commercially. Large-scale PIC integration has reached hundreds of components. Participating companies in PIC technology and industry include systems equipment manufacturers, optical device chip manufacturers, integrated service providers, semiconductor chip production and processing companies Foundry, and other fields, and are facing two major application markets for telecommunications and data.
Optical integration technologies include optical integration technology based on III-V cluster compound semiconductor materials, optical integration technology based on lithium niobate electrolyte materials, PIC technology based on SiO2 insulator materials, optical integration technology of silicon-based materials, and light based on polymer materials Integrated technology and optical integration technology based on silicon nitride materials. The light integration technology of III-V cluster compound semiconductor materials, such as GaAs and InP technologies, is particularly suitable for the integration of active devices such as light sources and detectors; the light integration technology of lithium niobate materials is particularly suitable for the development of high-speed light modulators. , optical switches, etc., with mature technology and large market share; PIC technology for SiO2 insulator materials, suitable for arrayed waveguide gratings, splitters, thermo-optical devices, and other passive optical waveguide devices The integrated light integration technology of silicon-based materials is similar to that of electronic integrated circuits, and is an important direction for future light integration and even photo-electric integration; polymer materials and silicon nitride materials also occupy the light integration and photonic device fields. A place. These integrated materials have their own strengths and have their own different application markets. Mixed integration of different devices, different functions, and different materials will be the short-term development direction of optical device technology.
PIC is the inevitable evolution direction of optical devices, and it will inevitably create a new generation of optical device-based application systems, and the final optical device development will be more integrated. III-V materials and silicon-based materials are more commonly seen in the industry as two major camps for future light integration technologies. In terms of materials, III-V materials are preferentially applied to active devices, and silicon-based materials are favored for passive devices. III-V materials are widely used in active devices. Indium phosphide is the only material that can realize large-scale monolithic integration of communication wavelengths. It still has potential for future development. The representative product is Infinera's high-speed light emission and reception. chip. However, indium phosphide is a rare material, and the epitaxial wafer has a small size, which is limited in low cost and large-scale production capacity. In addition, silicon photonics can apply the investment and technical experience on CMOS integrated circuits to the PIC field. Effectively reducing costs and increasing production efficiency have become one of the important technology directions of PIC in the future. Representative technologies of silicon photonics include Luxec's AOC chip, Cisco's CPAK optical module, Acacia's coherent CFP optical module, and Intel's hybrid integrated laser and chip-level optical interconnection technology. China also has a few companies. Get involved, but the scale is limited.
At the 2014 China Optical Network Symposium, Wei Leping, Director of the Science and Technology Committee of China Telecom Group, pointed out that optical devices are the bottleneck for the development of optical communications, and optical communications have become the slowest price reduction in all network composition technologies, in which the cost of optical devices is the bottleneck. bottleneck. Silicon photonics technology will become an important breakthrough direction. It uses the investment, facilities, experience, and technology of existing CMOS integrated circuits to design, manufacture, and package optical devices and optoelectronic integrated circuits. In terms of integration, manufacturability, and expandability Reached the CMOS level, resulting in breakthroughs in cost, power consumption, and size. Communication is an early application of silicon photonics technology. Just as transistors, integrated circuits, and lasers have historically been used, communication has often become an early application area for new technologies because of its high-tech properties. Then, as the technology and process mature, it will be extended to the mass consumption field to form a larger scale, further reduce costs, and then promote its popularity in the field of communications, forming a virtuous circle of technology.
Silicon photonics technology has no feasible technical route in terms of light sources. At present, it is mainly based on hybrid integration and short-range applications. It is continuously developing and mature, and will play an important role in the future. In short, whether it is indium phosphide or silicon photonics, it indicates that the optical communications industry is about to usher in profound changes and will significantly change the design and future of optical devices.

1, should continue to improve technology innovation and application of results
Improve industrial policies. According to the directory of research and industrialization encouraged by the State, combined with the actual situation of the enterprise, the government guides the direction and focus of investment through policies, and continues to maintain existing tax incentives for important imported equipment and materials that encourage projects, in the absence of alternative products in the country. Policies to actively support the innovation input and industrialization of national optical device companies;
2. Play the guiding role of financial funds and create a good investment and financing environment
Give full play to the guidance and promotion of various types of financial funds such as innovation funds, project center subsidies, special funds for technological transformation, and electronic development funds, promote industrial development, promote the establishment of government-oriented industrial investment funds, give play to the role of financial funds, and guide social resources to support the industry. The development actively promotes the integration of the enterprise and the capital market, and creates a favorable investment and financing environment for industrial development.
3. Improve industrial innovation capabilities and promote industrial upgrading
The innovation system of the optical device industry should be continuously improved. Relying on core enterprises, establish and perfect innovation platforms to provide support for enterprise innovation: Continue to promote technological transformation. Encourage enterprises to increase their investment in technology and strengthen their innovation base. Further promote the convergence of industrial basic research results with engineering and industrialization and enhance the core competitiveness of the industry. Through the formation of industrial alliances or technical cooperation alliances, we will promote upstream and downstream cooperation in the industrial chain, carry out joint research, improve product technology, and promote the promotion and application. Actively guide the transformation and upgrading of enterprises. To refine, energy saving and environmental protection development.
4. Strengthen the management of the industry and promote the healthy development of the industry
Develop industry development restraint mechanisms to prevent bad competition. Strengthen the solidarity and cooperation of domestic enterprises, hold groups to resist the impact of foreign enterprises to strengthen quality supervision, prevent the flow of counterfeit and inferior products into the market and disrupt the normal market order.
5. Strengthen the cultivation of high-end talents and actively participate in international exchange and cooperation
Focusing on the needs of high-end professional and technical personnel required for optical devices, the company has introduced top talents from the international community and has driven the innovation of high-end technologies in China's optical device industry. In particular, talents in the core chip and lC integrated circuit are to achieve independent innovation of high-speed chips and ICs, and to get rid of the core part of being subject to human conditions. Give full play to the role of industry associations, universities, research institutes, and various related social organizations, and cultivate various professional personnel at all levels for the continued development of the industry. Strengthen international exchanges and cooperation, actively participate in international standards work, and strengthen the right to speak in the field of international standards.
6. Strengthen core key technologies and product innovation
Key technology areas should strengthen core key technologies and product innovations, and increase research and development investment in key modulating light sources, semiconductor materials InP and Ploymer process research, high-speed chips, high-speed integrated circuits lC, and optoelectronic integration technologies; at 40G, 100G and 400G optical devices and core chips Next-generation PON optical devices and modules accelerate the development of key R&D technologies/products. Industrialization of 10GPON and 40G optical devices and module products, low-cost direct adjustment of 16×2.5Gb/s WDM fiber access chips, industrialization of transmission modules, industrialization of 100G and 400G devices and modules, and other major research and development efforts.
7. Improve the supporting measures for the industrial chain
We will vigorously develop the development of small and medium-sized private enterprises with original core technologies and their products/technology with independent intellectual property rights and innovation. Including relevant policies issued by the State and the province, entrepreneurship of scientific and technological personnel, transformation of scientific and technological achievements, government procurement of leading products of the industrial chain and other industrial supporting policies, reform of the government to take the lead, coordination of government operations related government departments, and formulate relevant policies to provide enterprises with Bright and efficient services are specifically for industry and commerce, taxation, quality inspection, safety, and environmental protection. At the same time, relevant tax reduction and exemption policies are formulated to reduce the burden on enterprises. For key enterprises, we will choose important project tracking support, from research and development to achievement transformation and industrialization, and provide full services to help companies become bigger and stronger.
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigarettesfactory.com