2016, VR first year, heavyweight manufacturers such as oculus, HTC, Sony, etc. have launched or announced their own consumer hardware products to seize the consumer market. I believe many of the VR enthusiasts have already started a Virtual reality device. Among these hardwares, the Oculus Rift CV1 (hereafter referred to as "CV1") is undoubtedly one of the most eye-catching hardware products. After all, it has a big event such as Facebook's $2 billion in 2014.
As we all know, Oculus Rift uses active optical positioning technology, how is it achieved?

(via:nukethefridge.com)
Basic implementation process:
There are hidden infrared lights (that is, marker points) hidden on the Oculus Rift device, which can emit infrared light and shoot in real time with an infrared camera. After obtaining the infrared image, the image captured by the camera is transmitted to the computing unit, and the useless information is filtered by the visual algorithm to obtain the direction of the infrared light, and then the PnP algorithm is used, that is, the four non-coplanar infrared lamps are utilized. The position information on the device and the image information obtained at the four points can finally incorporate the device into the camera coordinate system, fit the three-dimensional model of the device, and monitor the player's head and hand movement in real time.
Note: The specific picture can be seen as shown below, pay attention to the above red dots.
Next I will introduce you to my reasoning process and some details of the algorithm.
| LED lights on the head display
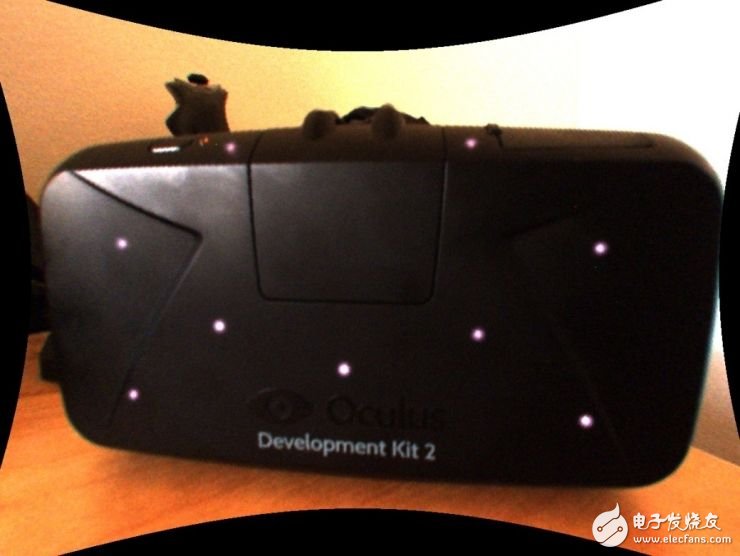

In the previous article, I mentioned that we need to use the position information of four non-coplanar infrared lamps on the device for positioning. If we want to know the position information of different infrared lamps on the device, we must be able to distinguish different infrared lamps. .
Why do you say this? If you don't distinguish between infrared lights, then when DK2 moves in space, the number of times that the camera will be associated (the process of optimal pose matching) will be very large after the camera captures the spot. , give a list:
1) If there are N prediction image points and M <<= N observation image points, there is N! /(NM)! Possible association
2) For N = 40 and M = 20 (for the number of DK2 LEDs), there is a correlation of 3.3 & TImes; 1029, so even a computer can't get results quickly.
Obviously, DK2 must use some a priori way to distinguish the light spots. So the question is, how is DK2 distinguished?
I have seen an article in the speculation that DK2 is distinguished by the LED lights, but it is not. Because it is relatively simple to distinguish by LED light, because the light and the light are most easily distinguished, but this method has a defect that it is impossible to distinguish whether the LED light caused by the posture change is blocked or the LED light itself is extinguished. Therefore, DK2 does not use this method, but uses the strength of LED lighting information to achieve. Let's observe the picture taken with a grayscale camera:
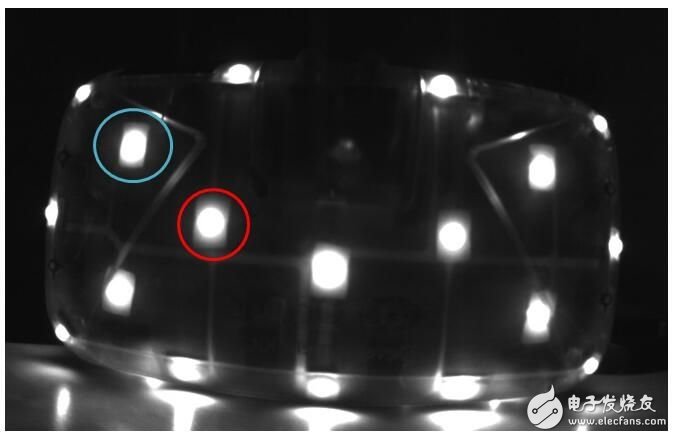
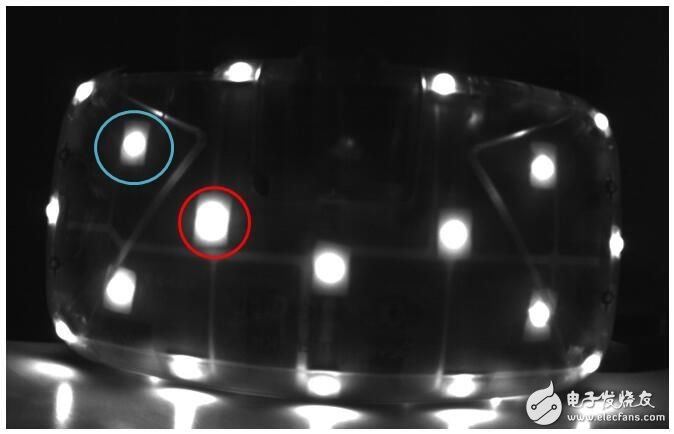
Comparing the above two figures, we can see that the size of the bright spots has changed. The red part can be seen, the spot is larger in Figure 2 and the opposite in blue. Let's take a look at the detailed approach. It must be said here that in the process of speculating the specific practice, I mistakenly thought that DK2 directly judged the spot size, and then judged the ID of the LED light according to the law of the multi-frame image, but in fact DK2 uses the difference method to judge the spot size. I am here to briefly introduce you to my reasoning process.
First of all, I took a lot of photos with my own camera and observed that if I shoot the camera at a frequency of about 60HZ, the image will repeat every 10th.
I will first give the spot a number, as shown below:
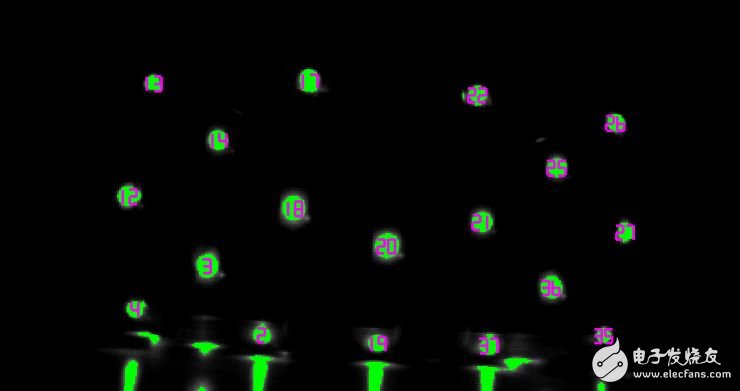
For example, the order of strength and weakness of point 2 can be identified by the naked eye: weak, weak, strong, strong, weak, strong, weak, weak, weak, strong.
So is this the case? How to express these strong and weak relationships in DK2?
First of all, the driver of the Windows SDK of the known SDK will send a start message to let the head display start to work;
Then, the driver will continue to receive the following information:

X1 X2 X3 X4 is a 32-bit number, which is the spatial coordinate obtained after image analysis (the principle is explained later), DX does not know what to do, but observe the above num, the conversion is 40, index starts from 1, Constantly incremented to 40, indicating that DK2 recognizes LED lights one by one. In addition, this information is sent once every 17ms, which is similar to the shooting frequency of 60HZ. It can basically be determined that one LED is used every 10 frames.
In order to fully determine this, another problem must also be identified: synchronization.
If it is really the LED that changes the ID of the LED light through 10 different changes, it must be synchronized.
This requires a synchronization signal to be transmitted to both the camera and the head display. If you know the timing of the synchronization, you know if it is 60Hz.
However, when I looked at the MT9V034 data, I found that the frequency of shooting was about 30HZ, but think about it, if you use differential detection, you can also use the 30HZ frequency to capture the change of light intensity. That is to say, DK2 does not directly judge whether the spot is large or small, but compares the spot of the current frame with the same spot of the previous frame. If it is larger than before, it is large, otherwise it is small. Then when a new frame arrives, the algorithm first extracts the bright pixel spots of the frame, as shown below. Ignore less than 10 pixels or not discs, and finally ensure that all the spots are from the large disc-shaped spots extracted in the previous frame and then compared.
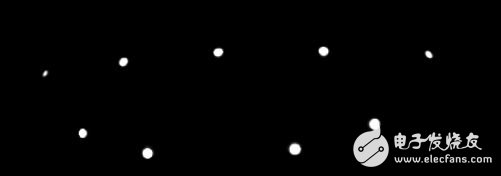
Therefore, DK2 compares the spot of the current frame with the same spot of the previous frame, and then allows the camera to determine the ID of the LED light according to different changes of 10 frames.
After further reviewing the correspondence between these points and location information, I concluded that the basis for DK2 to judge the strength and weakness is:
1) If the spot of the current frame is 10% larger than the spot of the previous frame, it is 0;
2) If the spot of the current frame is 10% smaller than the spot of the previous frame, it is 1;
3) Otherwise ignored.
This design is very good, preventing the LED lights from being randomly disturbed.
Introduction of LED indoor module: the indoor display above the market is composed of LED indoor module. LED module is a kind of product which is widely used in LED indoor module market. LED module is a kind of product which arranges LED together according to certain rules and orders. Vision display plays an important role in the market. LED modules are used in places where large screens need to be installed, such as stages, shopping malls, doorheads, etc.
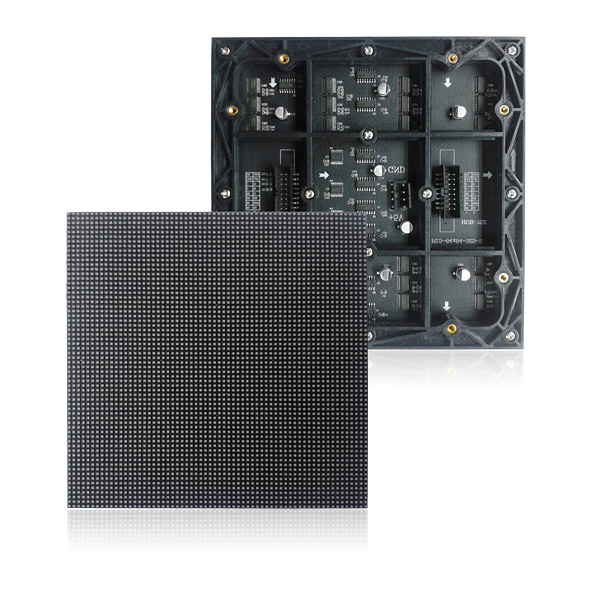
Here are some basic parameters of LED module
1. Color: at present, the main colors in the market are monochrome, full color and seven color single point control. Customers choose different colors according to the project requirements.
2. Voltage, the main voltage of the module is 5V, and the energy-saving module is 3.8V. The customer must be responsible for the power supply with accurate voltage during use, otherwise the module is easy to be damaged.
3. Working temperature: the normal working problem of LED is usually - 20 ° ~ 60 °. Under special requirements, it can be - 40 °. For other special environments, we will deal with it specially.
4. Point spacing: the LED point spacing is also the product model in the industry, and the point spacing is the distance between the center points of two lamp beads.
5. Brightness: This is an important parameter of the product. The visual display is higher than the industry standard level. It can be adjusted according to the requirements of the site.
6. Module size: module size refers to the length and width data of the module group.
8 Power: generally, the display screen has average power and maximum power. When leaving the factory, the most appropriate power will be set, and the required power can also be set according to customer requirements.
9. Refresh frequency: it means that the higher the refresh is, the better the image quality is. As a benchmark of the industry, the refresh is far higher than the industry standard.
The more mature the industry, the higher the requirements for products, the more popular customization, visual display, higher than the industry standard, the more mature customization, as long as you dare to think, we can help you achieve.

P2 Led Module,Indoor Led Module,P10 Led Display Module,Indoor Led Display Module
Shenzhen Vision Display Technology Co,.LTD , https://www.ledvdi.com