Whether it is applied to the LAN of the enterprise or the backbone network used in the data center, it is now developing towards high-density cabling to ensure broadband supply requirements and high-density network connection requirements. MPO/MTP multi-core cables are produced to meet high-density wiring. Especially in the process of 10G network migration to 40G/100G network, many network engineers will use MPO/MTP trunk cable as the preferred solution. However, the accuracy of the polarity in the MPO/MTP network system is guaranteed, and the design of the MPO/MTP cable polarity is very special. Below we discuss how to properly maintain the polarity of MPO/MTP.
What is polarity? Generally, an optical link requires two fibers to complete the entire transmission process. For example, the optical module includes a receiving end and a transmitting end. When used, it must ensure that the receiving end and the transmitting end are in an interconnected state, and the matching between the transmitting end (TX) and the receiving end (Rx) at both ends of the optical fiber link is Called polarity. In conventional wiring systems, connectors such as LC and SC are commonly used, and such connectors are easily matched, so there is no problem of polarity maintenance. However, for pre-terminated, high-density wiring systems, such as MPO/MTP connection systems, polarity issues must be highly valued.
Before discussing the maintenance of MPO/MTP polarity, we first come to know the MPO/MTP connector. The MPO connector is a multi-core multi-channel plug-in connector consisting of a pair of MT sleeves, two guide pins, two housings and an adapter. The standard feature is a standard diameter of 6.4mm x The guiding space of the 2.5mm rectangular ferrule end face and the guiding pin are positioned and centered. The MPO connector can be used for 2-12 core side-by-side fiber connections for up to two rows of 24-core fibers. When docked, a spring mounted on the ferrule tail applies an axial pressure to the ferrule until the outer frame of the connector is locked with the adapter. There is a male (convex) button on the upper side of the ferrule to limit the relative position between the connectors when connecting to determine the correct mating order of the fibers. In addition, the MPO connector has a male and female head, and the connector interface is connected by a female plug with a pinhole and a male plug with a guide pin and locked in an adapter. Due to its small size, high precision and high density, it is widely used in high-density and high-rate data centers.
The three polar methods specified by the TIA568 standard are called Method A, Method B, and Method C, respectively. In order to achieve the TIA568 standard, the MPO trunk cable is also divided into three types: straight-through, full-crossing, and cross-over, that is, Type A (key up - key down) and Type B (key up - key up/key down-key down completely). Cross), Type C (key up - key down line pair). These three MPO trunk cables and three polarity methods are described in detail below.
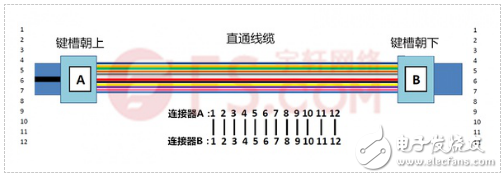
Straight-through MPO trunk cable: Straight-through MPO trunk cable uses straight-through cable, and the pre-terminated terminals at both ends are the MPU connector with the keyway upward and the MPO connector with the keyway facing downward. Therefore, the corresponding positions of the optical fibers at both ends of the cable are the same, that is, It is said that the position of the first core hole of the left connector corresponds to the position of the first core hole of the right connector. The following figure reflects the line sequence of the straight through MPO trunk cable:
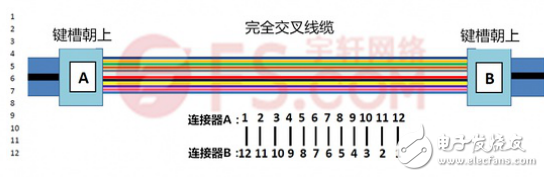
Fully crossover MPO trunk cable: Fully crossover MPO trunk cable uses reverse cable, both ends are pre-terminated with MPU connectors with keyway facing upwards. In this cable, the fiber at both ends of the cable corresponds to the opposite position. That is to say, the position of the first core hole of the machine on the left side corresponds to the position of the 12th core hole of the right connector, and the following figure reflects the line sequence of the completely crossed MPO trunk cable:
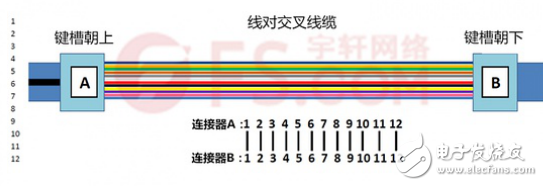
Wire-to-pair crossover MPO trunk cable: line-to-cross MPO trunk cable and straight-through MPO trunk cable, the pre-terminated terminals at both ends are the keyway-up MPO connector and the keyway-down MPO connector, but the online pair of crossover MPO trunks In the optical cable, the two optical fibers adjacent to one end of the optical cable are opposite to the corresponding two optical fibers at the other end, that is, the position of the first core hole of the left connector corresponds to the position of the second core hole of the right connector. The position of the second core hole of the left connector corresponds to the position of the first core hole of the right connector, and the following figure reflects the line sequence of the pair of crossed MPO trunk cables:
Different polar methods use different types of MTP trunk cables. However, all methods use duplex jumpers to form fiber links. The TIA standard also defines two different types of LC or SC duplex fiber patch cords for end-to-end duplex connections: AA (cross) jumpers and AB (straight through) jumpers.

This section will explain how to ensure the correct polarity of the MPO optical device connection under the TIA standard.
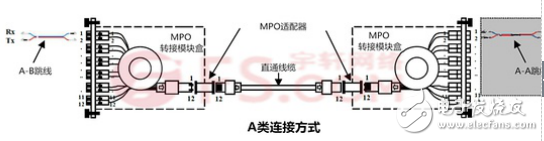
Type A connection: The following figure (Rx means reception, Tx means transmission) reflects the type A connection. The Type A connection uses a straight-through MPO trunk cable. To ensure polarity accuracy, two types of jumpers can be used: the standard duplex AB type jumper is used on the left side of the fiber link, and the AA type is used on the right side. Jumper.
Type B connection: The following figure reflects the B type connection. The Type B connection uses a fully crossed MPO trunk cable. Because the fibers at both ends of the fully crossed MPO trunk cable are opposite in position, the standard AB jumpers are used at both ends of the fiber link.
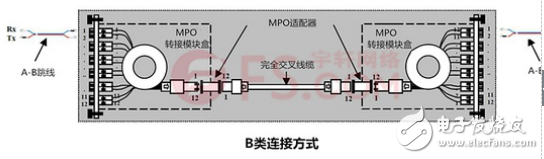
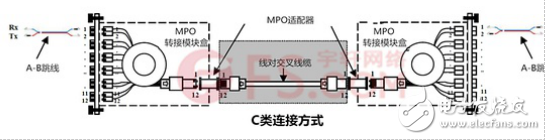
C type connection method: The following figure reflects the C type connection method. The C-type connection uses a line-to-cross MPO trunk cable, and both ends of the fiber link use a standard AB type jumper.
The polarity issues faced by network engineers using MPO/MTP products to meet the growing demand for high-speed transmission can be solved by choosing the right MPO cable, MPO connector and MPO adapter module box and jumper. A reliable high-density 40/100G transmission solution, first choose the preferred polarity method, and then choose the appropriate MPO/MTP optical device to support this polarity method.
48V25Ah Lithium Ion Battery,48V25Ah Lifepo4 Battery,48V Lithium Battery For Electric Scooter,48V25Ah Lithium Battery Pack
Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zttall.com